Logs and troubleshooting
Estimated reading time: 9 minutes
Did you know that Docker Desktop offers support for developers on a paid Docker subscription (Pro, Team, or Business)? Upgrade now to benefit from Docker Support. Click here to learn more.
Upgrade nowThis page contains information on how to diagnose and troubleshoot Docker Desktop issues, request Docker Desktop support, send logs and communicate with the Docker Desktop team, use our forums and Success Center, browse and log issues on GitHub, and find workarounds for known problems.
Troubleshoot
Choose  > Troubleshoot
from the menu bar to see the troubleshoot options.
> Troubleshoot
from the menu bar to see the troubleshoot options.
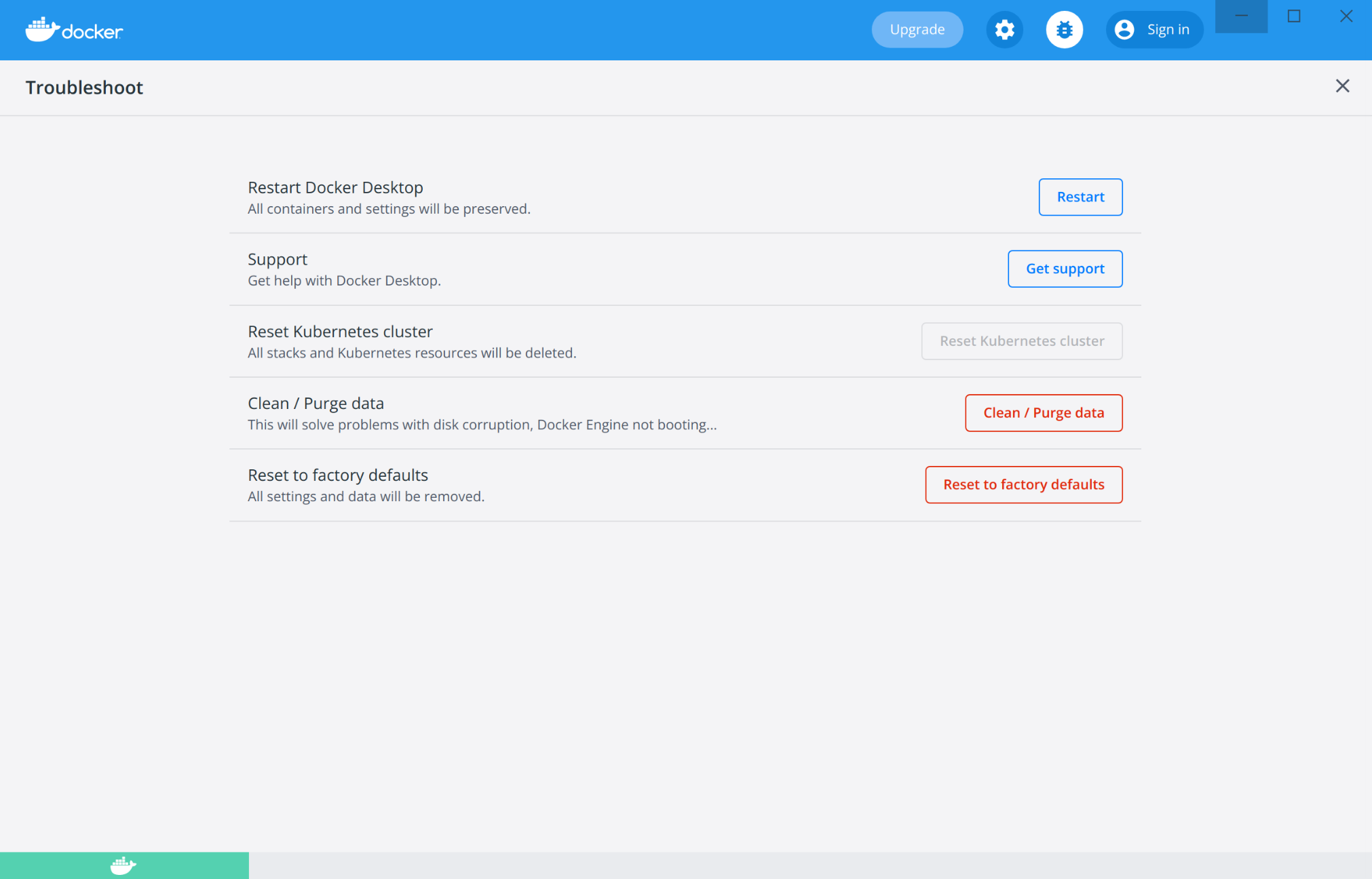
The Troubleshoot page contains the following options:
-
Restart Docker Desktop: Select to restart Docker Desktop.
-
Support: Users with a paid Docker subscription can use this option to send a support request. Other users can use this option to diagnose any issues in Docker Desktop. For more information, see Diagnose and feedback and Support.
-
Reset Kubernetes cluster: Select this option to delete all stacks and Kubernetes resources. For more information, see Kubernetes.
-
Clean / Purge data: This option resets all Docker data without a reset to factory defaults. Selecting this option results in the loss of existing settings.
-
Reset to factory defaults: Choose this option to reset all options on Docker Desktop to their initial state, the same as when Docker Desktop was first installed.
Diagnose and feedback
In-app diagnostics
If you encounter problems for which you do not find solutions in this documentation, on Docker Desktop issues on GitHub, we can help you troubleshoot the log data. Before reporting an issue, we recommend that you read the information provided on this page to fix some common known issues.
Note
Docker Desktop offers support for users with a paid Docker subscription. If you are experiencing any issues with Docker Desktop, follow the instructions in this section to send a support request to Docker Support.
Before you get started, we recommend that you sign into your Docker Desktop application and your Docker Hub account.
- Choose
 > Troubleshoot.
> Troubleshoot. - Optional: Sign into Docker Desktop. In addition, ensure you are signed into your Docker account.
- Click Get support. This opens the in-app Support page and starts collecting the diagnostics.
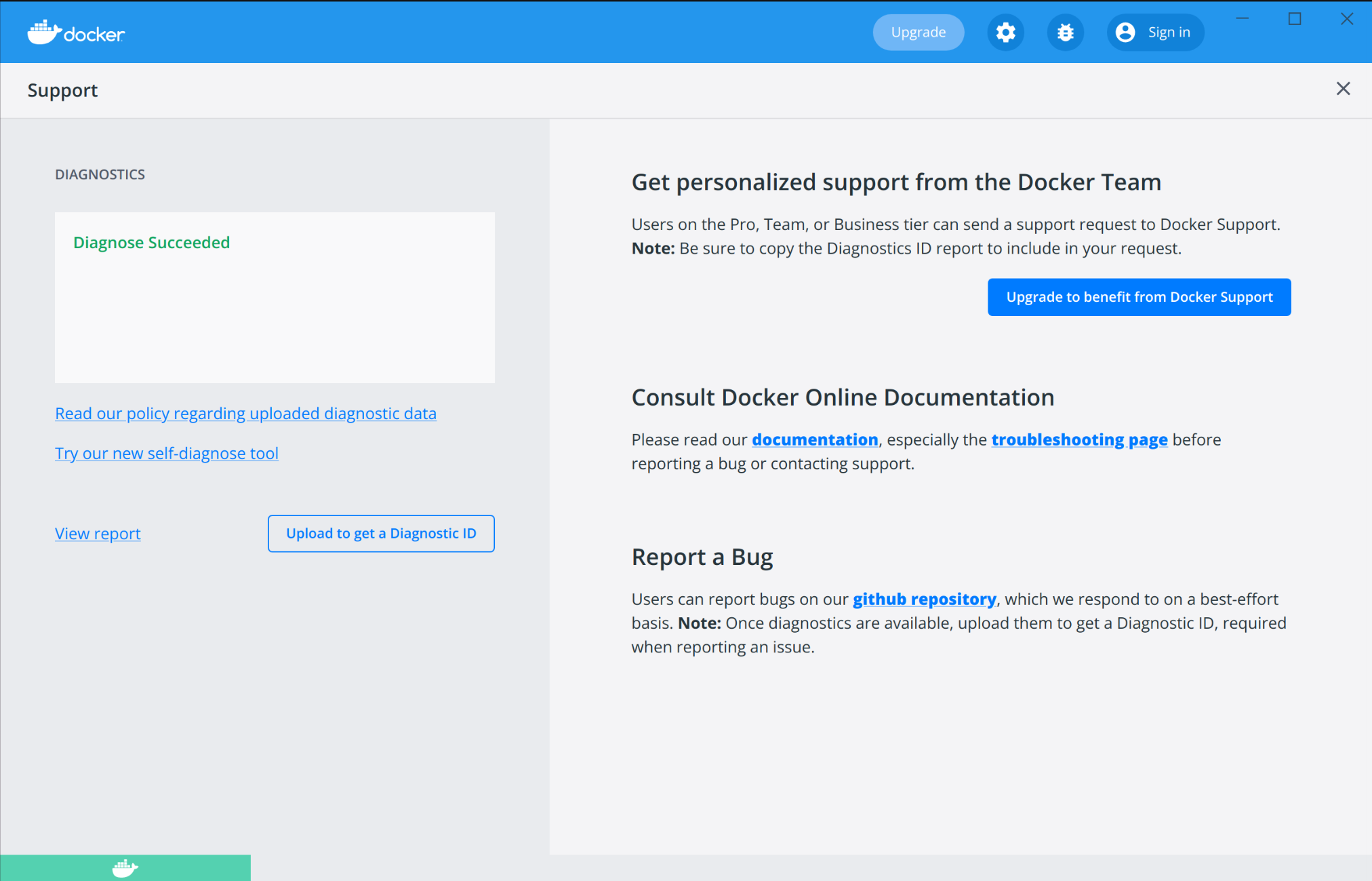
- When the diagnostics collection process is complete, click Upload to get a Diagnostic ID.
- When the diagnostics have been uploaded, Docker Desktop prints a diagnostic ID. Copy this ID.
- If you have a paid Docker subscription, click Contact Support. This opens the Docker Desktop support form. Fill in the information required and add the ID you copied earlier to the Diagnostics ID field. Click Submit to request Docker Desktop support.
Note
You must be signed in to Docker Desktop using your Pro, Team, or Business tier credentials to access the support form. For information on what’s covered as part of Docker Desktop support, see Support.
- If you don’t have a paid Docker subscription, you can click Upgrade to benefit from Docker Support to upgrade your existing account. Alternatively, click Report a Bug to open a new Docker Desktop issue on GitHub. This opens Docker Desktop for Linux on GitHub in your web browser in a ‘New issue’ template. Complete the information required and ensure you add the diagnostic ID you copied earlier. Click submit new issue to create a new issue.
Diagnosing from the terminal
In some cases, it is useful to run the diagnostics yourself, for instance, if Docker Desktop cannot start.
First, locate the com.docker.diagnose tool. If you have installed Docker Desktop in the Applications directory, then it is located at
/opt/docker-desktop/bin/com.docker.diagnose.
To create and upload diagnostics, run:
$ /opt/docker-desktop/bin/com.docker.diagnose gather -upload
After the diagnostics have finished, you should have the following output, containing your diagnostics ID:
Diagnostics Bundle: /tmp/B8CF8400-47B3-4068-ADA4-3BBDCE3985D9/20190726143610.zip
Diagnostics ID: B8CF8400-47B3-4068-ADA4-3BBDCE3985D9/20190726143610 (uploaded)
Diagnostics Bundle: /tmp/BE9AFAAF-F68B-41D0-9D12-84760E6B8740/20190905152051.zip
Diagnostics ID: BE9AFAAF-F68B-41D0-9D12-84760E6B8740/20190905152051 (uploaded)
The diagnostics ID (here BE9AFAAF-F68B-41D0-9D12-84760E6B8740/20190905152051) is composed of your user ID (BE9AFAAF-F68B-41D0-9D12-84760E6B8740) and a timestamp (20190905152051). Ensure you provide the full diagnostics ID, and not just the user ID.
To view the contents of the diagnostic file, run:
$ unzip –l /tmp/BE9AFAAF-F68B-41D0-9D12-84760E6B8740/20190905152051.zip
If you have a paid Docker subscription, open the Docker Desktop support form. Fill in the information required and add the ID to the Diagnostics ID field. Click Submit to request Docker Desktop support.
Self-diagnose tool
Docker Desktop contains a self-diagnose tool which helps you to identify some common problems. Before you run the self-diagnose tool, locate com.docker.diagnose. If you have installed Docker Desktop
in the Applications directory, then the self-diagnose tool will be located at
/opt/docker-desktop/bin/com.docker.diagnose.
To run the self-diagnose tool, run:
$ /opt/docker-desktop/bin/com.docker.diagnose check
The tool runs a suite of checks and displays PASS or FAIL next to each check. If there are any failures, it highlights the most relevant at the end of the report.
Feedback
Let us know your feedback on the self-diagnose tool by creating an issue in the desktop-linux GitHub repository.
Check the logs
In addition to using the diagnose and feedback option to submit logs, you can browse the logs yourself.
In a terminal
If you prefer to investigate issues yourself, you can access Docker Desktop logs by running the following command:
$ journalctl --user --unit=docker-desktop
You can also find the logs for the internal components included in Docker
Desktop at $HOME/.docker/desktop/log/.
View the Docker Daemon logs
Refer to the read the logs section to learn how to view the Docker Daemon logs.
Troubleshooting
Volume mounting requires file sharing for any project directories outside of $HOME
If you are using mounted volumes and get runtime errors indicating an application file is not found, access to a volume mount is denied, or a service cannot start, such as when using Docker Compose, you might need to enable file sharing.
Volume mounting requires shared drives for projects that live outside of the
/home/<user> directory. Go to  >
Settings > Resources > File sharing and share the drive that contains the Dockerfile and volume.
>
Settings > Resources > File sharing and share the drive that contains the Dockerfile and volume.
Workarounds for common problems
-
If
dockercommands aren’t working properly or as expected, you may need to unset some environment variables, to make sure you are not using the deprecated Docker Machine environment in your shell or command window. Unset theDOCKER_HOSTenvironment variable and related variables. If you use bash, use the following command:unset ${!DOCKER_*} -
For the
hello-world-nginxexample, Docker Desktop must be running to get to the web server onhttp://localhost/. Make sure that the Docker icon is displayed on the menu bar, and that you run the Docker commands in a shell that is connected to the Docker Desktop Engine. Otherwise, you might start the webserver container but get a “web page not available” error when you go tolocalhost. -
If you see errors like
Bind for 0.0.0.0:8080 failed: port is already allocatedorlisten tcp:0.0.0.0:8080: bind: address is already in use:- Run
lsof -i tcp:8080to discover the name and pid of the other process and decide whether to shut the other process down, or to use a different port in your docker app.
- Run
Support
This section contains instructions on how to get support, and covers the scope of Docker Desktop support.
Docker Desktop offers support for developers subscribed to a Pro, Team, or a Business tier. Upgrade now to benefit from Docker Support.
Upgrade nowHow do I get Docker Desktop support?
If you have a paid Docker subscription, please raise a ticket through Docker Desktop support.
Docker Community users can get support through our Github repos for-win, for-mac and desktop-linux where we respond on a best-effort basis.
What support can I get?
If you have a paid Docker subscription, you can request for support on the following types of issues:
- Desktop upgrade issues
- Desktop installation issues
- Installation crashes
- Failure to launch Docker Desktop on first run
- Usage issues
- Crash closing software
- Docker Desktop not behaving as expected
- Configuration issues
- Basic product ‘how to’ questions
What is not supported?
Docker Desktop excludes support for the following types of issues:
- Use on or in conjunction with hardware or software other than that specified in the applicable documentation
- Running on unsupported operating systems, including beta/preview versions of operating systems
- Running containers of a different architecture using emulation
- Support for the Docker engine, Docker CLI, or other bundled Linux components
- Support for Kubernetes
- Features labeled as experimental
- System/Server administration activities
- Supporting Desktop as a production runtime
- Scale deployment/multi-machine installation of Desktop
- Routine product maintenance (data backup, cleaning disk space and configuring log rotation)
- Third-party applications not provided by Docker
- Altered or modified Docker software
- Defects in the Docker software due to hardware malfunction, abuse, or improper use
- Any version of the Docker software other than the latest version
- Reimbursing and expenses spent for third-party services not provided by Docker
- Docker Support excludes training, customization, and integration
What versions are supported?
We currently only offer support for the latest version of Docker Desktop. If you are running an older version, you may be asked to upgrade before we investigate your support request.
How many machines can I get support for Docker Desktop on?
As a Pro user you can get support for Docker Desktop on a single machine. As a Team, you can get support for Docker Desktop for the number of machines equal to the number of seats as part of your plan.
What OS’s are supported?
Docker Desktop is available for Linux, Mac and Windows. The supported version information can be found on the following pages:
Can I run Docker Desktop on Virtualized hardware?
No, currently this is unsupported and against the terms of use.
linux, troubleshooting, logs, issues